Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A infection is an acute disease of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus. The virus is spread from person to person by the faecal-oral route (that is, ingestion of something that has been contaminated with the faeces of an infected person). The virus is shed in the faeces of infected people, and household or sexual contacts of cases may become infected. Symptoms include fever, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain and jaundice. Some people experience a fairly mild illness and recover within a couple of weeks. Other people develop more severe symptoms and may take months to fully recover. Older people are more likely to have more severe symptoms and some infected children do not have any symptoms at all. Hepatitis A became notifiable in 1981.
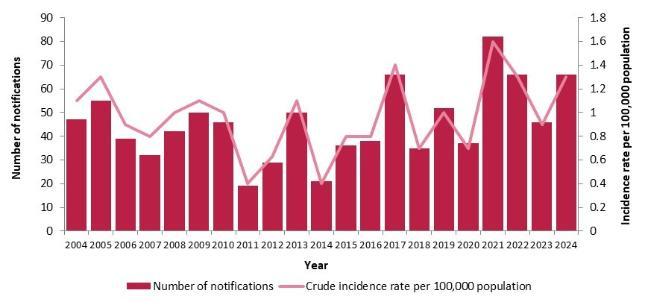
Number of hepatitis A notifications and notification rate per 100,000 population, 2004-2024
Last updated: 23 July 2025
What is hepatitis A?
Hepatitis A infection is an acute self-limiting disease of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus.
What are the symptoms of hepatitis A?
- Many people, particularly young children, do not develop any symptoms. In general, the severity of the disease increases with age.
- The most common symptoms are fever, loss of appetite, nausea, fatigue and abdominal pain, followed within a few days by jaundice.
- Clinical severity varies from a relatively mild illness lasting 1-2 weeks to a severely disabling illness lasting months.
- Prolonged relapsing hepatitis for up to one year occurs in 15% of cases. Chronic (long-term) infection does not occur.
- A small proportion of cases develop a severe overwhelming hepatitis. Death is estimated to occur in 0.1% to 0.3% of cases, although this increases to 1.8% in adults >50 years of age.
What is the incubation period for hepatitis A?
The incubation period (time from infection to onset of symptoms) is 15 to 50 days, the average being 28 days.
How is hepatitis A spread?
Hepatitis A virus is primarily spread from person to person by the faecal-oral route (that is, ingestion of something that has been contaminated with the faeces of an infected person). It may also be spread through food that has been contaminated by infected food handlers or by contaminated water. The virus is shed in the faeces of infected people. They are most infectious in the week or two before onset of symptoms and may be infectious up to one week after onset.
Where is hepatitis A a problem?
Hepatitis A infection occurs worldwide, but the risk of infection varies with the levels of sanitation and personal hygiene. Ireland is considered a low incidence country. Over the past decade the number of reported cases per year has ranged from 20 to 50, with occasional small, local outbreaks. Hepatitis A is now rare in Western Europe, North America, Japan, New Zealand and Australia.
How is an infection diagnosed?
Hepatitis A is diagnosed by testing the patient's blood or stool for the presence of specific anti-viral antibodies. The viral RNA can also be detected in blood or stool.
Can hepatitis A be treated?
There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A. Therapy should be supportive and aimed at maintaining comfort and adequate nutritional balance.
How can hepatitis A infection be prevented?
Preventive measures for hepatitis A include:
- Good personal hygiene, with special emphasis on careful hand-washing after using the toilet and before preparing and eating food.
- Clean water and good sanitation, with sanitary disposal of faeces.
- Immunisation through the administration of vaccine and/or human normal immunoglobulin (HNIG) in certain situations (see below)
Is hepatitis A a notifiable disease?
Hepatitis A is a notifiable disease under the Infectious Diseases Regulations. Cases should be notified to the Medical Officer of Health.
Hepatitis A vaccination
There is a safe and effective vaccine available for hepatitis A. It is available either as a vaccine on its own, or combined with hepatitis B vaccine. Recommendations for the use of vaccine and HNIG to prevent secondary cases and outbreaks are detailed in the Immunisation Guidelines for Ireland. Vaccination is recommended for those at increased risk, including:
- Travellers to high-risk areas (Africa, Asia, Central and South America, Eastern Europe and the Middle East)
- Susceptible people with chronic liver disease
- People with haemophilia and recipients of plasma-derived clotting factors
- People who inject drugs
- Men who have sex with men
- Laboratory workers who may be exposed to hepatitis A
- People in recent close contact with infected individuals.
Other risk groups may also be considered for immunisation and are listed in the Immunisation Guidelines for Ireland.
Travel advice
Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for travellers to certain countries in Africa, Asia, Central and South America, Eastern Europe and the Middle East. Further information is available from Fit For Travel
Further information on Hepatitis A:
ECDC: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/hepatitis-a
CDC: http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HAV/index.htm
Man2Man.ie: http://man2man.ie/stis/hepatitis-abc/
Sexualwellbeing.ie: https://www.sexualwellbeing.ie/sexual-health/sexually-transmitted-infections/types-of-stis/hepatitis-a-in-msm.html
Last updated: 19 September 2017
Case definition
Hepatitis A (acute) infection (Hepatitis A virus)
Clinical criteria* (for probable case)
Any person with a discrete onset of symptoms (e.g. fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, intermittent nausea and vomiting)
AND
At least one of the following three:
- Fever
- Jaundice
- Elevated serum aminotransferase levels
Laboratory criteria
At least one of the following three:
- Detection of hepatitis A virus nucleic acid in serum or stool
- Hepatitis A virus specific IgM antibody response
- Detection of hepatitis A virus antigen in stool
Epidemiological criteria
At least one of the following four:
- Human to human transmission
- Exposure to a common source
- Exposure to contaminated food/drinking water
- Environmental exposure
Case classification
A. Possible case
NA
B. Probable case
Any person meeting the clinical criteria and with an epidemiological link
C. Confirmed case
Any person meeting the laboratory criteria
*Note: Asymptomatic cases are common in young children
Current as of: 28 May 2018



