Genital Herpes simplex
Genital Herpes simplex
Genital herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two HSV types: type 1 and type 2. Type 2 is most commonly associated with genital infection. Type 1 has also been found to cause genital infection but is more commonly associated with oral herpes (‘cold sores’).
Genital herpes is common in Ireland. It is mostly diagnosed in young women.
For information, advice and support on sexual health visit sexualwellbeing.ie
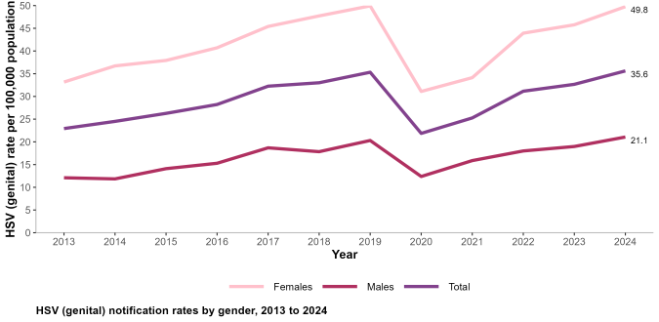
1,834 cases notified in 2024
35.6 the national notification rate per 100,000 population.
Last updated: 3 June 2025
Case Definitions
Herpes simplex (genital) (Herpes simplex virus)
Clinical criteria
Any person with the following clinical picture: herpes simplex (genital) is a condition characterised by visible, painful genital or anal lesions. Clinical presentation may be atypical.
Laboratory criteria
At least one of the following four:
- Detection of herpes simplex virus nucleic acid (HSV 1 or HSV 2), in clinical specimens from anogenital lesion
- Isolation of herpes simplex virus from cervix, urethra, or anogenital lesion
- Demonstration of virus by antigen detection technique in clinical specimens from cervix, urethra, or anogenital lesion
- Demonstration of multinucleated giant cells on a Tzanck smear of scrapings from an anogenital lesion
- Epidemiological criteria
NA
Case classification
A. Possible case
NA
B. Probable case
A clinically compatible case (in which early infectious syphilis has been excluded by appropriate tests) with either a diagnosis of genital herpes based on clinical presentation (without laboratory confirmation) or a history of one or more previous episodes of similar genital lesions
C. Confirmed case
A clinically compatible case, including an atypical presentation, that is laboratory confirmed
Current as of: 01 July 2025



